AWS Transit Gateway: Everything You Need to Know
For organizations using cloud providers like AWS, efficient network infrastructure is essential for delivering robust cloud-based solutions. AWS Transit Gateway plays a crucial role in simplifying and streamlining cloud network connectivity. In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of AWS Transit Gateway and how it can benefit your organization’s cloud network. We also describe applications for AWS Transit Gateway Flow Logs and transit gateway equivalents provided by other cloud vendors (Google Cloud Router and Azure Virtual WAN).
What is AWS Transit Gateway?
AWS Transit Gateway is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that simplifies cloud infrastructure management. It acts as a central hub that connects multiple Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and on-premises networks through a single gateway, making it easier to scale and maintain your network architecture. Acting as a highly scalable, cloud-based router, AWS Transit Gateways (or “TGW”s) simplify network architecture and enable efficient traffic routing between different environments.
Transitioning to cloud quickly complicates networking. Learn the top 3 AWS gotchas and how to avoid them.

How do Transit Gateways work?
A Transit Gateway functions as a virtual router, connecting multiple AWS VPCs and VPN connections within a single AWS account or across multiple accounts. It enables you to establish secure connections between your VPCs and on-premises networks, reducing the need for complex configurations and multiple connections. To better understand how Transit Gateways work, let’s delve into some key components and functionalities:
Centralized routing and connectivity
Transit Gateways handle all routing and connectivity between the connected AWS VPCs and VPNs. This centralized management eliminates the need for individual connections between each VPC and VPN, resulting in a more efficient and streamlined network.
Inter-region communication
Transit Gateways support communication between VPCs and VPNs located in different AWS regions. This allows you to build a robust, global network infrastructure that can serve users around the world while minimizing latency.
Multi-account support
AWS Transit Gateway supports multi-account networking, enabling you to connect Amazon Virtual Private Clouds and VPNs from different AWS accounts. This flexibility allows organizations to consolidate their networks and improve collaboration between departments or teams with separate AWS accounts.
Cloud Visibility: Kentik Cloud Enhancements for AWS
Transit Gateway Architecture
AWS Transit Gateway architecture revolves around key concepts such as route propagation, attachments, MTU, and transit gateway route tables. Let’s dive deeper into each specific component:
AWS Transit Gateway Attachments
AWS Transit Gateway Attachments are the connections between the Transit Gateway and the VPCs or VPNs. Each attachment represents a link between a specific VPC or VPN and the Transit Gateway, allowing for efficient traffic routing.
Transit gateway Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU)
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is the largest data packet size that can be transmitted across a network. AWS Transit Gateway supports an MTU of up to 8500 bytes, enabling efficient data transfer across your cloud network.
Transit gateway route table and default route table
A Transit Gateway route table contains a set of rules that determine how traffic is routed between various VPCs and VPN connections attached to the Transit Gateway. Each Transit Gateway has a default route table, and you can create additional custom route tables for more granular control over traffic routing.
Associations
Associations are the links between Transit Gateway route tables and attachments. When you associate a route table with an attachment, it dictates how traffic is routed between that specific AWS VPC or VPN connection and the rest of the network.
Route propagation
Route propagation enables automatically updating Transit Gateway route tables based on the routing information from the VPCs and VPN connections attached to the Transit Gateway. This ensures that your network routing remains up-to-date and efficient as your cloud infrastructure evolves.
Benefits of AWS Transit Gateway
AWS Transit Gateway offers several key benefits that can enhance your network infrastructure and architecture, including simplified network architecture, increased scalability, centralized control, and improved security. Let’s explore these benefits in more detail:
Simplified network architecture
By consolidating multiple VPC and VPN connections through a single gateway, AWS Transit Gateway significantly simplifies your cloud network architecture, making it easier to manage and maintain. This streamlined approach reduces the number of network components you need to manage, resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective solution.
Increased scalability
AWS Transit Gateway enables you to scale your network connections easily as your organization grows. You can add or remove VPCs and VPN connections without reconfiguring your entire network. This flexibility helps you adapt your network infrastructure to meet changing business requirements and accommodate growth.
Centralized control
With a single point of control for routing and connectivity, AWS Transit Gateway makes managing your cloud network more efficient and less time-consuming. This centralized management allows you to monitor and maintain your network more effectively, making it easier to troubleshoot issues and optimize performance.
Improved security
AWS Transit Gateway enhances your cloud infrastructure security by consolidating all VPCs and VPN connections under a single gateway, making it easier to enforce consistent security policies across your entire network. This unified approach enables you to effectively implement network segmentation, access control, and traffic filtering, reducing the risk of security breaches and data leaks.
Reduced operational complexity
AWS Transit Gateway reduces the operational complexity of managing large-scale cloud networks by automating route propagation and configuration management tasks. This automation minimizes manual intervention, reducing the likelihood of human error and freeing up valuable resources to focus on other critical tasks.
Why are Transit Gateways important?
Transit Gateways are essential in today’s cloud-driven world as they provide a streamlined approach to managing network connectivity across VPCs and VPNs. This centralization simplifies network architecture and reduces the overhead associated with maintaining multiple connections. By offering a single point of control, Transit Gateways enable organizations to enforce consistent security policies, improve network performance, and scale their infrastructure efficiently.
Transit Gateway Use Cases
AWS Transit Gateway offers various use cases to meet the diverse needs of organizations. Let’s take a closer look at some specific functions and contexts where Transit Gateways shine:
Multi-VPC connectivity
Transit Gateway simplifies multi-VPC connectivity by connecting multiple VPCs through a single gateway. This eliminates the need for complex peering configurations and allows organizations to manage and monitor their entire network from a centralized location.
Global application delivery
With the support of AWS Transit Gateway, organizations can deliver applications globally by connecting VPCs and on-premises networks across different regions. This ensures low-latency access to applications and resources for users around the world.
Seamlessly handle surges in demand
Transit Gateway enables organizations to quickly scale their network infrastructure to accommodate surges in demand. By easily adding or removing VPCs and VPN connections, organizations can maintain optimal performance and handle increased workloads without compromising security or network efficiency.
Transit Gateway vs VPC Peering
While both Transit Gateway and VPC Peering enable network connectivity between VPCs, they differ in terms of scalability, manageability, and use cases. VPC Peering establishes a direct connection between two VPCs, which is suitable for smaller-scale deployments. However, as the number of VPCs grows, the complexity of managing multiple peering connections increases exponentially. On the other hand, Transit Gateway simplifies this process by consolidating all VPC connections through a single gateway, offering better scalability and centralized management.
AWS Transit Gateway and VPC Flow Logs
AWS introduced VPC Flow Logs for Transit Gateway in 2022 to provide deeper visibility and insights into network traffic on Transit Gateways. This feature allows organizations to monitor and analyze traffic traversing through Transit Gateway, a central hub that interconnects multiple VPCs and on-premises networks. VPC Flow Logs are a feature that captures and records network traffic metadata within an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
VPC flow logs capture detailed metadata about the traffic flowing through various components of your network, such as VPCs, subnets, and network interfaces. By analyzing flow logs, organizations can gain insights into network behavior and detect anomalies, using the data for troubleshooting, capacity planning, security compliance, and threat detection.
Kentik Cloud users can collect, analyze, and visualize flow logs generated on AWS Transit Gateways (in addition to cloud VPC flow logs and other network data sources for cloud and hybrid environments, such as NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, J-Flow, and sFlow-RT logs). By consuming flow logs generated on AWS Transit Gateways, Kentik Cloud provides a unified view of traffic across VPCs and facilitates centralized monitoring and analysis. A few of the use cases for Transit Gateway Flow Logs—and how Kentik enables them—are described below.
Troubleshooting and Performance Optimization
With Transit Gateway Flow Logs, you can detect patterns or anomalies across multiple Amazon Virtual Private Clouds to identify and troubleshoot issues that span multiple environments. The logs capture detailed information about network traffic, including source and destination IP addresses, ports, protocols, and packet counts. Analysis of these logs helps to identify performance bottlenecks and optimize network routing and capacity, thus improving network performance.
Network Capacity Planning
Kentik’s Data Explorer allows for comparing performance across different time periods based on the metrics and attributes captured in Transit Gateway Flow Logs. Analyzing historical logs helps identify usage trends and peak traffic periods and forecast future network capacity requirements. It aids in efficient capacity planning and resource allocation, such as upgrading capacity or redistributing traffic among new VPCs or Direct Connects.

Security Compliance and Threat Detection
Transit Gateway Flow Logs offer visibility into network traffic, enabling the detection of potential security threats or anomalies. Unusual traffic patterns, unauthorized access attempts, or communication with blocklisted IP addresses can be detected and flagged through Kentik Alerts. Alerts can also flag activities like port scanning before they impact your organization.
Auditing and Compliance
Transit Gateway Flow Logs assist in auditing network communications and maintaining compliance with security policies. By analyzing the logs, you can granularly track historical network activity, generate audit trails, and import enriched flow data to your SIEM for added context, which can help meet regulatory requirements and conduct post-incident investigations.
To learn more about these features and use cases, see “How can I use Kentik Cloud’s AWS Transit Gateway Flow Log support?” in this Kentik blog post.
For a more comprehensive understanding of VPC flow logs, refer to our blog post, “VPC Flow Logs in AWS: How to Monitor Traffic at the Edge of Your Cloud Network”.
AWS Direct Connect and Transit Gateway
AWS Direct Connect is a service that establishes a dedicated network connection between an organization’s on-premises data center and AWS. AWS Transit Gateway can be integrated with AWS Direct Connect to enable a high-performance, private connection between your VPCs and on-premises networks. This integration can improve performance, lower latency, and increase security by bypassing the public internet.
AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) and Transit Gateway
AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) is a service that allows you to share AWS resources across multiple AWS accounts. When working with AWS Transit Gateway, you can use RAM to share a single Transit Gateway with other accounts, simplifying the process of connecting VPCs and VPNs across multiple AWS accounts. This approach can help organizations improve resource utilization, reduce complexity, and manage costs more effectively.
NAT Gateway vs AWS Transit Gateway
While discussing AWS Transit Gateway, it’s useful to understand another common networking component within the AWS ecosystem: the NAT Gateway.
What is a NAT Gateway?
A NAT (Network Address Translation) Gateway is a managed service provided by AWS that allows EC2 instances in a private subnet to initiate outbound network traffic to the internet or other AWS services, but prevents unsolicited inbound traffic from reaching those instances. It’s designed to provide high availability and bandwidth, automatically scaling up to 45 Gbps of bandwidth.
How Do NAT Gateways Relate to AWS Transit Gateways?
-
Traffic Routing: Both AWS Transit Gateway and NAT Gateway deal with routing traffic. While the Transit Gateway focuses on inter-VPC and on-premises network connectivity, the NAT Gateway deals with outbound internet connectivity for private resources.
-
Network Architecture: In complex AWS architectures, you might find both Transit Gateways and NAT Gateways working in tandem. For example, while Transit Gateway connects multiple VPCs, a NAT Gateway in each VPC can ensure instances have appropriate outbound internet access.
-
Security Considerations: Using NAT Gateway ensures that your private instances are not directly exposed to the internet, enhancing security. Meanwhile, Transit Gateway offers a centralized control plane for routing, further strengthening network security and simplifying management.
When Would You Use NAT Gateway with AWS Transit Gateway?
If you have a multi-VPC architecture connected via AWS Transit Gateway and need instances in private subnets to access the internet (e.g., for software updates), you’d employ a NAT Gateway. In such a scenario, the NAT Gateway would handle the outbound internet traffic, while the Transit Gateway would manage inter-VPC and VPN traffic.
Transit Gateway Pricing and Cost Optimization
Understanding the pricing model for AWS Transit Gateway is essential for effective cost management. AWS charges for Transit Gateway based on the number of attachments, data processing, and data transfer. To optimize costs, organizations can:
- Monitor and analyze network traffic to identify and eliminate redundant or underutilized connections.
- Implement traffic filtering and prioritization to ensure efficient use of available bandwidth.
- Regularly review Transit Gateway configurations to ensure they align with the organization’s requirements and cost goals.
How to Reduce Transit Gateway Costs
AWS Transit Gateways, like NAT Gateways, operate as a metered service. Metered services like Transit Gateway charge not only for the service itself but also based on the volume of data transferred through it. The charge for a Transit Gateway is based on the volume of data processed, hourly charges based on the number of attachments, and inter-region data transfers. Unchecked, these costs can accumulate rapidly, especially in large-scale, multi-region deployments.
Strategies for reducing Transit Gateway costs include:
-
Monitor Traffic Patterns: Use tools like Kentik to gain visibility into your Transit Gateway traffic. By understanding where the most expensive traffic flows occur, you can optimize routing and reduce unnecessary data processing costs.
-
Optimize Data Transfers: Consolidate data transfers and leverage regional data processing to minimize inter-region transfer fees. Routing traffic through the most cost-effective paths can also significantly cut down expenses.
-
Control Attachments and Configurations: Regularly review and optimize the number of VPC and VPN attachments to ensure they align with your organization’s needs without incurring unnecessary costs.
-
Proactive Monitoring and Alerts: Implement real-time monitoring and alerting systems, like those provided by Kentik, to detect and respond to cost anomalies before they lead to budget overruns. This proactive approach ensures you maintain control over your Transit Gateway costs.
For a deeper exploration of AWS Transit Gateway cost management strategies, see our blog post “Understanding and Controlling AWS Transit Gateway Costs with Kentik”.
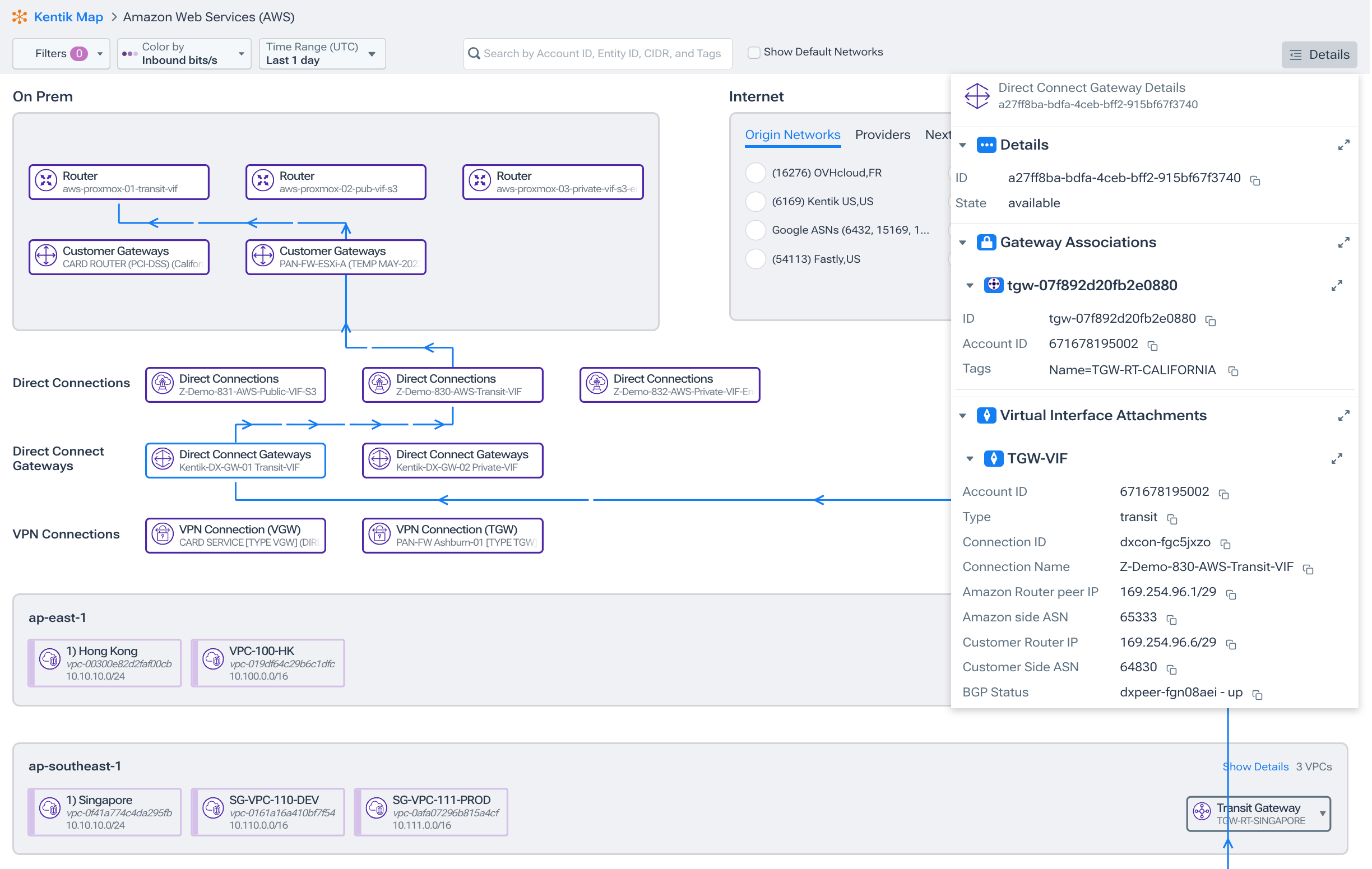
Monitoring Transit Gateway Traffic and Costs with Kentik
In this short video, Phil Gervasi demonstrates how to use Kentik to visualize AWS topology and understand the traffic going over AWS Transit Gateways—which is one of the key contributors overall cloud costs. He drills into a specific AWS Transit Gateway to look at traffic metrics for that gateway, identify egress traffic, identify attachments, and look at gateway metrics over time.
Transit Gateway and Network Performance Monitoring and Observability
Monitoring and optimizing network performance is essential to ensure high availability and a seamless user experience. NetOps professionals can use AWS-native tools like Amazon CloudWatch and VPC Flow Logs, or third-party monitoring solutions like Kentik for Amazon Web Services, to gain insights into Transit Gateway performance, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues. These tools can also help with capacity planning, traffic engineering, transit gateway cost optimization, and performance optimization efforts.
AWS Transit Gateway Alternatives: Google Cloud Router and Azure Virtual WAN
While AWS Transit Gateway is an excellent solution for organizations using Amazon Web Services, other cloud providers—such as Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure—have similar offerings. Understanding these alternatives can help you make informed decisions when choosing the best solution for your cloud network infrastructure.
Google Cloud Router
Google Cloud Router is a fully managed, global software-defined networking service that connects your Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks to on-premises networks or other VPCs via Cloud VPN or Cloud Interconnect. It provides dynamic routing using the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to exchange routes between networks, ensuring optimal traffic routing and high availability.
Key features of Google Cloud Router include:
- Dynamic routing: Cloud Router uses BGP to dynamically learn and propagate routes, simplifying network management and ensuring efficient traffic flow.
- Global scope: Cloud Router is available globally, allowing you to manage and optimize routing across different regions.
- High availability: Cloud Router automatically manages failover in case of VPN tunnel failures, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
Microsoft Azure Virtual WAN
Microsoft Azure’s Virtual WAN is a networking service that simplifies large-scale, geographically distributed connectivity and routing by providing a fully managed, global network infrastructure. It allows you to connect and route traffic between Azure Virtual Networks (VNets), on-premises networks, and remote users using VPNs or ExpressRoute circuits.
Key features of Azure Virtual WAN include:
- Centralized management: Azure Virtual WAN provides a single, unified dashboard for managing and monitoring your global network, simplifying network operations.
- Scalability: Azure Virtual WAN enables you to easily scale your network by adding or removing connections as needed, accommodating growth and changing requirements.
- Traffic optimization: Azure Virtual WAN uses Microsoft’s global network to route traffic efficiently, ensuring low latency and high availability.
- Secure connectivity: Azure Virtual WAN supports multiple security features, including end-to-end encryption, network segmentation, and firewall integration.
Discover the Benefits of Transit Gateway Observability with Kentik
Solutions like AWS Transit Gateway, Google Cloud Router, and Microsoft Azure Virtual WAN simplify and streamline cloud network management, offering increased scalability, centralized control, and improved security. By leveraging these services, organizations can easily handle multi-VPC connectivity, global application delivery, and surges in demand.
To gain deeper insights into your network performance and further optimize your cloud infrastructure, consider adopting a network observability platform like Kentik. Kentik is widely used for visibility, monitoring, and cost optimization across major cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. By providing comprehensive visibility and actionable insights into network traffic, performance, and costs, Kentik enables organizations using AWS Transit Gateway and similar solutions to make data-driven decisions and improve how they manage cloud networks.
To get started, request a demo or sign up for a free trial today.