JFlow Analysis
What is JFlow?
JFlow is a flow-based monitoring protocol developed by Juniper Networks, designed to provide detailed insights into network traffic patterns and usage. Similar to other flow-based monitoring protocols such as NetFlow and sFlow, JFlow collects and aggregates traffic data, enabling network administrators and engineers to analyze and optimize the networks performance, capacity, and security.’
JFlow captures and exports traffic flow data from routers and switches, providing essential information about the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, packet and byte counts, and other traffic-related details. This data is then sent to a flow collector, which processes and stores the information for further analysis. Network engineers can use this data to identify bandwidth usage, monitor application performance, detect security threats, and optimize network resource allocation.
How JFlow Helps Network Engineers
The ability to characterize IP traffic and understand how and where it flows is critical for assuring network availability, performance, and security. JFlow (also known as “J-Flow” or “jFlow”) analysis is the practice of using tools to perform monitoring, troubleshooting and in-depth inspection, interpretation, and synthesis of traffic flow data.
Analyzing JFlow facilitates more accurate capacity planning and ensures that resources are used appropriately in support of organizational goals. It helps network operators to determine where to apply Quality of Service (QoS) policies as well as how to optimize resource usage, and it plays a vital role in network security to detect Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks and other undesirable network events and activity.
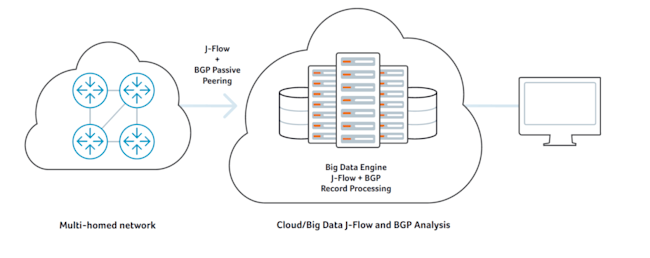
Overcoming Common Network Challenges with JFlow Analysis
JFlow analysis offers insight to overcome many common challenges encountered by network operators, managers, and engineers including:
- Monitoring major contributors of network traffic: Network engineers can easily see top talkers and listeners on the network.
- Understanding application traffic volume and its network impact: An example is identifying unusual application network loads such as video content or large file transfers. JFlow statistics can also be used to measure how application and policy changes affect costly WAN traffic.
- Optimizing internet peering relationships: Organizations operating BGP peerings to maintain multi-homed connectivity to the internet can utilize JFlow data fused with BGP routing data to perform sophisticated peering analysis and optimize their peering arrangements. This can help to improve service quality, reduce peering costs, or even uncover new revenue opportunities as a result of usage pattern analysis.
- Troubleshooting and understanding network pain points: JFlow analytics can be used to diagnose slow network performance, recognize bandwidth hogs or misconfigurations, and characterize bandwidth utilization quickly via the intrinsic representation of traffic totals and traffic details.
- Detecting unauthorized WAN traffic: By analyzing JFlow, it becomes possible to avoid costly upgrades to expensive WAN services by identifying the applications causing congestion, verifying legitimacy, and adjusting delivery policies to mitigate any adverse impact on higher-value concurrent traffic streams.
- DDoS and anomaly detection: JFlow can also be used for detection of DoS/DDoS and other types of network behavior anomalies.
- Validating QoS parameters: Because JFlow includes all packet priority markings, it can be used to confirm that appropriate bandwidth has been allocated to each Class of Service (CoS) and that no CoS is over or under-subscribed.
JFlow Analysis Use Cases
Various organizations such as network operations, engineering, planning, architecture, and security can use JFlow analysis as a primary source of intelligence. Proper use of JFlow analysis can reduce the number of hardware and software technologies needed to manage networks. This reduces network administration costs and enhances cross-organizational collaboration and communications and help cross-functional teams get the most out of network investments.
Network Planning and Analysis
JFlow data provides key information for sophisticated analysis to optimize both strategic network planning (e.g., who to peer with, backbone upgrade planning, routing policy planning) as well as tactical network engineering decisions (e.g., adding additional VIPs to routers, upgrading link capacity) — minimizing the total cost of network operations while maximizing network performance, capacity and reliability.
Network Monitoring
JFlow data enables extensive, near real-time network monitoring capabilities. Flow-based analysis techniques may be used to visualize traffic patterns associated with individual routers and switches as well as on a network-wide basis (providing aggregate traffic or application based views) to provide proactive problem detection, efficient troubleshooting, and rapid problem resolution. Analysis of JFlow can be used as a basis for real-time alerting, improving network operators’ ability to react quickly and accurately to any major service disruptions as well as get early warning indicators of potential performance and service quality degradations that warrant proactive intervention.
Application Monitoring and Profiling
JFlow data enables network managers to gain a detailed, time-based, view of application usage over the network. Any common JFlow tool can be used to recognize applications by port/protocol. Content and service providers may utilize this information to plan and allocate network and application resources (e.g., web server sizing and location) to responsively meet customer demands. Enterprises can use these same insights to understand application dependencies and resource consumption.
User Monitoring and Profiling
JFlow data enables network operators to gain detailed understanding of customer/user utilization of network and application resources. This information may then be utilized to efficiently plan and allocate access, backbone and application resources as well as to detect and resolve potential security and policy violations.
Additional Aspects of JFLow Analysis
NetOps professionals should also be aware of the following aspects of JFlow analysis:
Integration with Other Monitoring Tools
JFlow analysis can be integrated with other network monitoring tools and platforms to provide a more comprehensive view of the network. By combining JFlow data with information from SNMP, syslog, and performance monitoring solutions, NetOps professionals can gain deeper insights into the overall health and performance of their networks.
Network Scalability and Flexibility
As networks grow and become more complex, the importance of scalable and flexible monitoring solutions increases. JFlow analysis can accommodate the growth of a network by handling large amounts of traffic data and adjusting to changes in network topology. This ensures that NetOps professionals can continue to rely on JFlow for accurate and actionable insights as their networks evolve.
Customization and Reporting
JFlow analysis tools often provide customizable reporting features, allowing NetOps professionals to tailor reports and dashboards to their specific needs. This enables the creation of targeted and relevant visualizations that can aid in decision-making and streamline network management tasks.
Automation and Alerting
JFlow analysis tools can be configured to automate various tasks, such as generating reports, sending notifications, or triggering specific actions in response to predetermined conditions. This can help NetOps professionals proactively address potential issues and ensure the network remains agile and responsive to changing demands.
Security and Compliance
JFlow analysis can be an essential component of a network security strategy, helping NetOps professionals detect and mitigate potential threats, such as DDoS attacks or unauthorized access attempts. Additionally, JFlow data can be used to demonstrate compliance with various industry standards and regulations by providing detailed insights into network traffic and usage patterns.
More Reading About JFflow
At Kentik, we’ve taken JFlow, NetFlow, IPFIX and sFlow analysis to big data scale and offered it as an easy to use SaaS. Learn more about traffic flow analysis from these blog posts:
Learn more about Kentik’s SaaS Big Data JFlow analysis, network performance monitoring and DDoS protection solution.


